In the beginning, streamers had a hard time getting the stream quality they wanted due to the restrictions of platforms like Twitch. The first version of Twitch surfaced in 2007, a spin-off of the Justin.tv platform – capturing the life of founder Justin Kan via a camera fitted to a baseball cap, but the platform we all know and love did not become a reality until 2011. When Justin.tv transitioned into the Twitch platform, any user could create their own live stream broadcast by encoding footage of their gaming using PC hardware, and transmitting it to Twitch servers.
Gamers all over the world were eager to show off their talents to a new audience of followers, and saw the platform gaining 20 million users within a year. As the Twitch user base increased, different parts of the platform’s architecture began to reach limitations, which ranged from database storage caps to chat capacity, right through to search and discovery. Engineers lament on the Twitch blog how these architectural changes proved to be the best move for the growing company.
CPU and GPU Streaming Technology
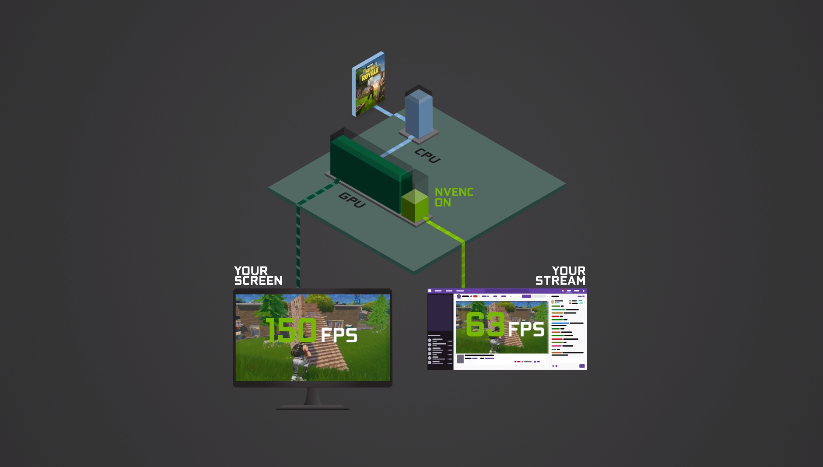
At this point, the pressure was on Twitch to allow for seamless growth, but also on CPU and GPU manufacturers to produce technologies that the market demanded. NVIDIA soon adopted the stance of market leaders in 2012, with the release of the Kepler-based GeForce 600 series, which provided streamers with the all important NVENC (Nvidia Encoder), which made streaming HD gaming footage a breeze. NVENC also allowed users to make use of open source broadcasting applications such as OBS – a ubiquitous streaming software still used over ten years later. Turing and Ampere architectures use different generations of NVENC, with third generation Tensor Cores in Ampere GPUs offering higher performance versus second generation Tensor Cores in Turing GPUs.
AMD’s own encoding engine, Video Code Engine (VCE), was also hitting the market at roughly the same time, with the Radeon HD 7000 Series. Although a dominant force in the gaming market in 2011, AMD could not compete with the NVENC technology, which left some gamers who wanted to stream their footage on Twitch a little out in the cold. VCE was later succeeded by Video Core Next (VCN), with the latest VCN 4.0 video engine (in RDNA 3-based GPUs) able to rival NVIDIA in the encoding arena for the first time.
Besides the GPU market, Intel and AMD were making changes to their processors to enable much faster and easier content creation. This growing market was wide open, and not to be overlooked in consumer CPUs, as this type of usage had previously only seen in higher end processors for professional creators. Now, almost every gamer wanted to stream, and every streamer wanted a capable CPU and GPU.
In 2022, CPUs and GPUs feature a wealth of specifications for Twitch users, content creators and of course – gamers. The best gaming and streaming PCs offer NVENC or VCN encoding, high speed ethernet and WiFi, and components designed to deliver stunning visuals that can be streamed live in full HD to any platform that supports it.
Which graphics card is good enough for gaming?
By definition, all dedicated graphics cards are capable of gaming, but the older the card – the more limited your performance will be. An ideal starting point is the GTX 1650, which is a great entry level GPU (as we will discuss further into this article), but a superb mid-tier graphics card for casual and hardcore gamers – an all-rounder – is the NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3060.
Whilst this graphics card will not future-proof you for playing the latest games in a few years time at highest settings, it will certainly allow you to enjoy high framerates and smooth visuals. The RTX 3060 is a ‘Jack of all trades‘ playing AAA titles, simulator games, competitive titles, content creation and streaming.
RTX 3060 Benchmarks
AVG. FPS: ULTRA SETTINGS / 1920×1080
- Ghostwire: Tokyo – 129 FPS
- Cyberpunk 2077 (1.5) – 64 FPS
- Elden Ring – 60 FPS
- Dying Light 2 – 60 FPS
- Rainbow Six: Extraction – 157 FPS
- God of War – 53 FPS
- Halo Infinite – 82 FPS
- Forza Horizon 5 – 66 FPS
- New World – 96 FPS
The RTX 3060 is one of the most popular at Chillblast, featuring in the spec of many of our customisable gaming PCs. One of the most popular RTX 3060 builds is the Chillblast Fusion Crystal Lite RTX 3060 Gaming PC which features the Alder Lake 12th-Gen budget masterpiece, the Intel Core i5-12400F and 16GB DDR4 2666MHz to get the best performance in games and productivity.

Which graphic card is best for budget gaming?
Taking all of the above into consideration, and with the pedigree of both AMD and NVIDIA, there are plenty of options for graphics cards that will handle modern titles. The entry level NVIDIA GeForce GTX 1650 is a perfect example of how a solid graphics card can stand the test of time, and with NVIDIA’s Game Ready Drivers, the support for the graphics card has been excellent as new games are released.
With a limited budget, the GTX 1650 – when paired with a 12th-Gen processor – makes an ideal entry level gaming PC, and will allow you to stream in HD on Twitch or YouTube. The GTX 1650 is capable of playing titles such as Minecraft, League of Legends, DOTA2, Hearthstone and CS:GO, as well as more demanding games like Overwatch 2, GTA5, the FarCry series, Battlefield V, Call of Duty and more.
At Chillblast, there are a few options for the GTX 1650, with budget gaming PCs that offer all of the above, built with the Award Winning workmanship of our expert team of PC engineers.
Which is better GTX or RTX?
Although GTX has its merits for lower end gaming, RTX offers much more for gamers, streamers and creators. For video editing PCs, graphic design workstations and other creative systems, RTX really shows its mettle – but more so in gaming.
The most applauded aspect of these features is the Ray Tracing capabilities of RTX GPUs. Ray tracing acceleration is a technology that developers implement in their games via NVIDIA OptiX, Microsoft DXR, and Vulkan ray tracing API. By using these libraries, developers can create stunning lighting and shading in games, with reflective surfaces that mimic real life.

Along with Ray Tracing, RTX offers Artificial Intelligence (AI) technologies which accessed by developers using the NVIDIA NGX SDK. Development studios can utilise AI to increase the performance of their games, putting less strain on the graphics processor, and being much more efficient when calculating extremely complex visuals.
DLSS (Deep Learning Super Sampling) is another breakthrough technology from NVIDIA which uses AI to upscale lower resolution graphics to 1080p or 4K (and beyond). Tensor Cores – specialised cores that compute massive calculations efficiently – are responsible for taking a smaller resolution image and increasing the resolution, and producing higher framerates on a display. The Super Sampling aspect is the anti-aliasing of the calculated images, which creates smooth visuals as well as higher framerates per second.
For more information on the technical specification of RTX, visit NVIDIA’s developer site or their RTX consumer information page.
Which graphics card is best for streaming?
Streaming demands a lot from a gaming PC, and a solid CPU is also required to handle both priority tasks and background tasks. The majority of the workload falls to the graphics card, however, and the powerful NVENC encoder in NVIDIA RTX graphics cards means your CPU will only need to handle productivity tasks such as chat windows, internet browsing and other background activity as you manage your stream.
NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3080
With the Ampere-based RTX 3080, you effectively have a home studio at your fingertips, with NVIDIA Broadcast and NVENC encoder. By using the RTX 3080 in a broadcast, you can expect triple-digit framerates while you play, and your viewers will see a flawless 60+ FPS high definition stream on Twitch or YouTube.

View RTX 3080 Streaming PCs
NVIDIA GeForce RTX 4090
The latest and greatest graphics card from NVIDIA, the RTX 4090 delivers unparalleled performance in gaming. The new GPUs use Ampere architectures to deliver ground-breaking framerates and graphics quality. DLSS 3 ensures stunningly smooth framerates by using AI technology to “splice” generated frames into the visuals. This creates an overall more lifelike and natural result.
For streaming, the RTX 4090 makes use of the latest NVENC technology to push the limits of your game’s framerates, while delivering the highest possible FPS in your HD stream.







